5 min read time
Table of Contents

Explaining Soft Tissue Injuries in Vehicle Collisions
Soft tissue injuries, which include strains, sprains, bruises, and whiplash, are among the most common yet often overlooked consequences of car accidents.
Even when symptoms appear only hours or days after impact, prompt medical evaluation is essential to identify and treat these injuries effectively.
Defining Soft Tissue Damage
Soft tissue damage refers to injury to muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels, not bones.
Common symptoms of soft tissue injuries include strains, sprains, bruises, and whiplash, which are often caused by rapid acceleration or deceleration forces caused by a car accident.
Soft tissue injury symptoms typically appear within 24‑48 hours after a car accident and present as soreness, swelling, discoloration, and a limited range of motion.
How Car Accidents Cause Soft Tissue Injuries
When a car accident occurs, the occupants of the vehicles involved experience a sudden change in velocity that forces their bodies to move abruptly.
The sudden deceleration or acceleration stretches muscles, tendons, and ligaments beyond their normal range, creating micro‑tears and inflammation.
This mechanical strain often manifests as whiplash, wrist or ankle sprains, or back and neck strains, even when the vehicle’s structure remains intact.
Because a soft tissue injury is often invisible to the victim at first, prompt medical evaluation is essential to prevent chronic pain and long‑term mobility loss, so ensure you never skip seeking medical treatment when sustaining soft tissue injuries in a car accident, even if you believe it to be minor.
Common Soft Tissue Injuries Seen in Car Accidents
In car accidents, a range of injuries can occur, from minor bruises to more serious soft‑tissue damage.
Understanding the common soft tissue injuries helps in early recognition and timely medical care. These injuries often include sprains, strains, bruises, and whiplash.
Sprains and Strains
A sprain occurs when a ligament stretches or tears, often at a joint such as the knee or ankle, producing pain, swelling, and limited motion. A strain involves overstretching or tearing of a muscle or tendon, leading to muscle spasms, soreness, and reduced strength.
Whiplash
Whiplash happens when a rear‑end collision forces the head and neck to snap forward and back, overstretching ligaments and muscles.
Symptoms such as pain, stiffness, and headaches often appear hours later, and, if untreated, can lead to chronic pain and limited motion, so early medical care is vital.
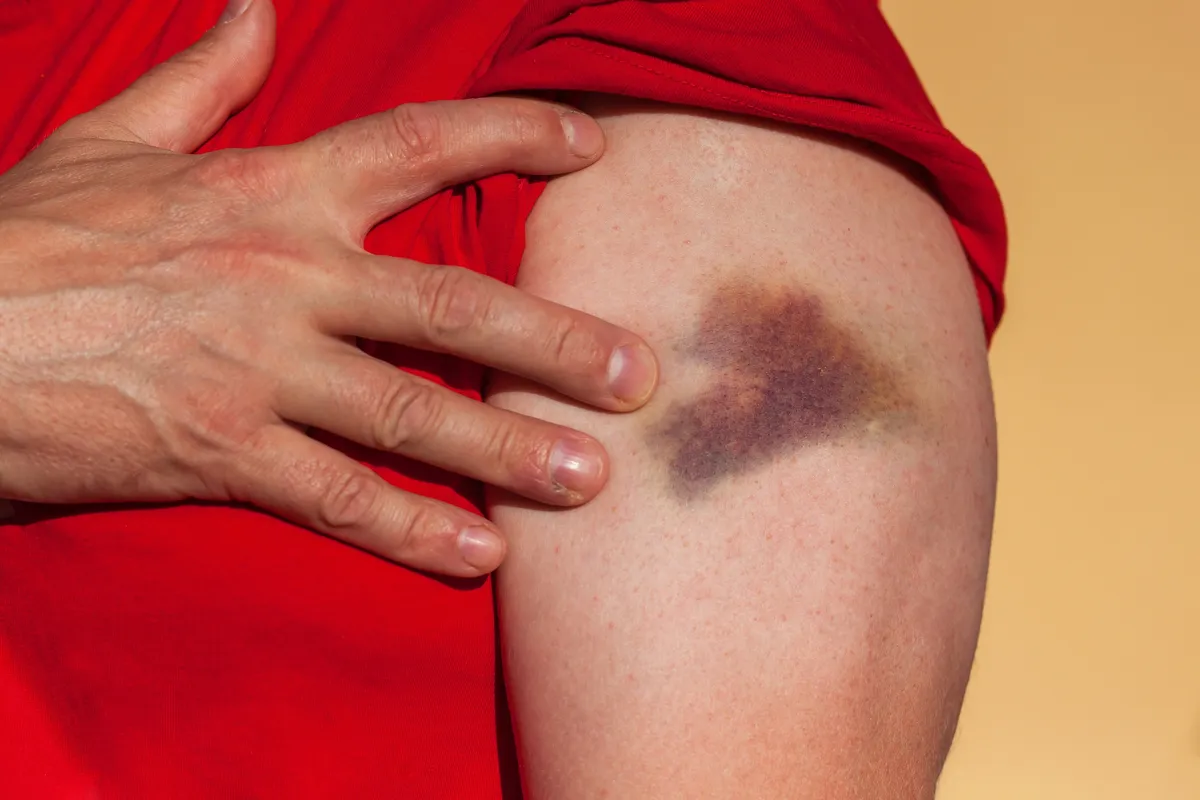
Contusions (Bruises)
Contusions, or bruises, result from blunt force trauma during a car collision, such as impact against a dashboard or seat belt.
Doctors diagnose them by visual inspection and may order imaging if swelling suggests deeper injury; most heal on their own, though early care can prevent complications.
Some contusions may require stitches if the skin is lacerated.
Symptoms and Signs of Soft Tissue Injuries To Watch For
After a car accident, many accident victims may overlook subtle cues that hint at soft tissue damage.
Recognizing early discomfort, stiffness, or tingling can prompt one to seek timely medical attention and prevent chronic issues.
By staying alert to these early signs, you can address potential injuries before they worsen.
Delayed Onset Pain
After a car accident, many drivers feel fine at the scene but develop pain later.
Delayed onset pain often begins 24 to 48 hours after impact and can take over a week to fully develop, especially in cases of whiplash and soft-tissue strains.
Prompt medical evaluation can prevent the progression to chronic pain and reduce long‑term disability.
Even mild symptoms warrant a check‑up, as untreated soft‑tissue injuries may worsen with movement, driving, or sleep, leading to persistent stiffness, limited mobility, and a wide range of other problems.
Swelling and Tenderness
Swelling and tenderness are common early signs of soft‑tissue damage after a car wreck.
Even if you feel fine at the scene, inflammation can develop within 24–48 hours, making the affected area painful to touch and visibly puffy.
Persistent swelling may point to a sprain or strain, while localized tenderness often accompanies a contusion. Prompt medical evaluation helps differentiate these injuries and prevents chronic pain or reduced mobility.
Medical Evaluation and Treatment Options
When soft tissue injuries arise from a motor vehicle collision, a thorough medical evaluation is essential to identify the extent of ligament, tendon, or muscular damage.
Once diagnosed, a range of treatment options from conservative measures like RICE and ice packs held for 20 minutes, the initial rest period, to minimally invasive measures such as arthroscopy can be considered.
In some cases, surgery, commonly called rotator cuff surgery, may be recommended, especially for significant rotator cuff tears.
Defining the Initial Rest Period
The initial rest period following a car accident can reduce swelling and stabilize injured tissue, allowing subsequent treatments to be more effective.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
A large portion of soft tissue injuries are frequently easily treated with targeted physical therapy.
Minimally invasive measures such as arthroscopy may be used for shoulder injuries, and the goal is to restore function with the least disruption possible.
Imaging and Diagnostics
If swelling or tenderness is significant, MRItests are often ordered to visualize ligament tears, such as an ACL tearor torn MCL, and to assess for blood vessel injury that may cause hidden bleeding.
Closed head injuries can coexist with soft tissue damage; therefore, a comprehensive evaluation that includesclosed head injuries is recommended to prevent seemingly minor injuries from worsening.
Visit an Orthopedic
In cases where a shoulder or upper arm injury is severe, an orthopedic consult may be necessary.
Surgery, commonly called rotator cuff surgery, is considered when conservative therapy does not yield adequate improvement. The procedure can involve minimally invasive measures such as arthroscopic release of a torn rotator cuff.
Other ligament injuries, such as an ACL tear, can also result from sudden impact jolts during a collision. Likewise, a torn MCL may occur in rear‑end collisions, especially when the knees are forced to twist.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of soft tissue injury management.
Patients with shoulder impingement are treated to improve neck and shoulder muscles, while those with ACL or MCL tears focus on joint stability exercises.
Many soft tissue injuries are frequently easily treated with a consistent home‑exercise program.
Take Legal Action After a Soft Tissue Injury
Soft tissue injury claims can be complex, as insurance companies may not automatically recognize the full extent of your pain and recovery needs.
However, with the help of an experienced car accident attorney from the Rodney Okano Car Accident Lawyer, you can ensure fair compensation, as our car accident attorneys will guide you through the process of filing a soft tissue injury claim and negotiating with insurers.
Additionally, we maintain an official record of all medical treatments, which is critical for establishing the legitimacy of your insurance claims.
Our Nevada legal team can also assist in identifying delayed symptoms that might otherwise be overlooked, ensuring they are incorporated into the official record.
Schedule a free consultation with an experienced Las Vegas car accident attorney from our law firm today by calling (702) 566-3600 to discuss your case and determine the best course of action.
Obtain the Compensation You're Entitled To
Contact Us Today
Rodney Okano Car Accident Lawyer is a Las Vegas personal injury law firm with over 20 years of experience helping clients obtain maximum compensation following injuries from accidents such as car crashes, worksite injuries, and slips and falls. Over those years, The Rodney Okano Car Accident Lawyer Law Firm has become an experienced law firm that can ensure exceptional results for any of its clients.